
More than a quarter of the population snores on a regular basis, according to the National Sleep Foundation.
Snoring is problematic because it can be a symptom of an underlying medical problem that needs treatment, and because it can be terribly disruptive to the rest of the household.
Why do people snore?
There are all kinds of reasons why a person might snore.
-
Allergies irritate and swell the upper airway and cause congestion, which can lead to snoring.
-
Dry air and climates, or areas where there is a lot of dust or pollution, can leave you feeling congested; this is because the mucus membranes line the upper airway and nasal passages with mucus to filter out particle matter.
-
Weight gain means tissues and fat deposits around the neck may swell, creating "wind resistance" in the airway.
-
Smoking irritates the tissues in the throat, leading to inflammation that can cause snoring.
-
Alcohol relaxes the muscles of the upper airway, which can become floppy and make noise as you breathe during sleep.
-
Medications can also relax the tone of the muscles in the neck and chest, making the work of breathing more difficult.
-
Aging itself is a reason to snore: the older our bodies get, the less tone and moisture we hold in our tissues.
-
The physiology of the upper airway may create a natural environment for snoring. Overlarge organs like the tongue or tonsils might get in the way of breathing, or a soft chin or deviated septum may create the proper conditions for snoring.
-
Your sleeping position has an impact on whether you snore. Most wives who have husbands who snore general find they are sleeping on their backs as they snore, but with a nudge to turn them to the side, the snoring lightens up or ceases altogether.
-
Sleep deprivation can lead to snoring, believe it or not. It has to do with how "hard" you sleep following a period of sleeplessness. Recovery sleep may lead to excessive snoring due to fatigue and a persistent sleep drive.
-
An underlying sleep disorder like insomnia or obstructive sleep apnea could be to blame. Insomnia happens to people who consistently wake up several times a night; sometimes, people who have frequent nighttime awakenings are actually suffering from unidentified (and, therefore, untreated) sleep apnea.
Why should we treat snoring?
Snoring is the 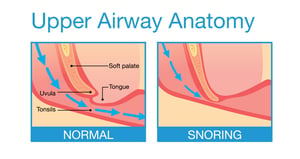 sound that occurs in the back of the nose and throat when air inhaled or exhaled comes into contact with tissues in a way that creates vibrations.
sound that occurs in the back of the nose and throat when air inhaled or exhaled comes into contact with tissues in a way that creates vibrations.
Despite snoring being a widespread problem, it's not actually normal to snore; snoring signals that something is wrong with the way we are breathing as we sleep.
The benefits of treating snoring
There are a number of reasons to take your snoring seriously:
-
Snoring treatment results in lower blood pressure.
-
Snoring treatment relieves other adverse side effects, such as sleep deprivation, morning headaches, sore throat, and daytime sleepiness.
-
Snoring treatment spares your bed partner. You may not realize how disruptive your snoring is, but it may have a serious impact on your spouse.
-
You will feel better and have more energy. Snoring tends to fragment sleep and leads to feeling tired all the time, as well as less motivated and focused.
How is snoring treated?
There are several options for treating snoring, once you admit it's a problem and realize it's worthwhile to treat.
Lifestyle
Your sleep breathing can be improved by your application of these lifestyle changes:
Humidity from a nightstand device can keep the upper airway passages moist and reduce congestion.
device can keep the upper airway passages moist and reduce congestion.
Weight loss shrinks the fatty deposits in the neck; exercise helps return tone to the tissues of the upper airway, leaving you with more space to breathe without obstruction.
Body position has a big impact on snoring. People who sleep on their sides are less likely to snore then those who sleep on their backs or stomachs.
Tranquilizers, sleeping pills, and antihistamines should not be used at bedtime, as they have the power to further depress the respiratory system.
Time your alcohol consumption to at least four hours before bedtime. Alcohol relaxes the tissues and muscles, resulting in snoring.
Avoid heavy meals or snacks at least three hours before going to bed. These can lead to problems with heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which can irritate the throat and lead to snoring.
Establish regular sleeping patterns to ensure you are not sleep deprived.
Surgery
There are several surgical procedures to treat snoring, some of them outpatient, in which physicians remove the excess tissue in and around the mouth, upper airway, and nasal passages in order to provide a more open space for airflow during sleep. Other procedures involve implanting supports in the soft palate in order to help keep the tone quality high so that snoring can't take place.
Appliances
There are dozens of different kinds of mouthpieces used for the treatment of snoring. They more or less work in the same way. Either they retain the tongue so it does not slide into the back of the throat and cause vibrations, or they splint open the airway by advancing the lower jaw, creating extra space for unimpeded airflow.
Be tested
It's important to rule out underlying medical illness or unidentified sleep disorder as the culprit behind your snoring. In particular, while snoring does not always lead to sleep apnea, almost all people with sleep apnea snore. Sleep apnea and snoring have a relationship that should not be ignored.
In the case of sleep apnea, an overnight test can confirm whether your airway is being obstructed as you sleep, which leads to oxygen depletion in the blood supply at night if left untreated. Over the long term, unchecked sleep apnea can lead to many different serious medical problems, such as stroke, obesity, high blood pressure, heart disease, cancer, and more.
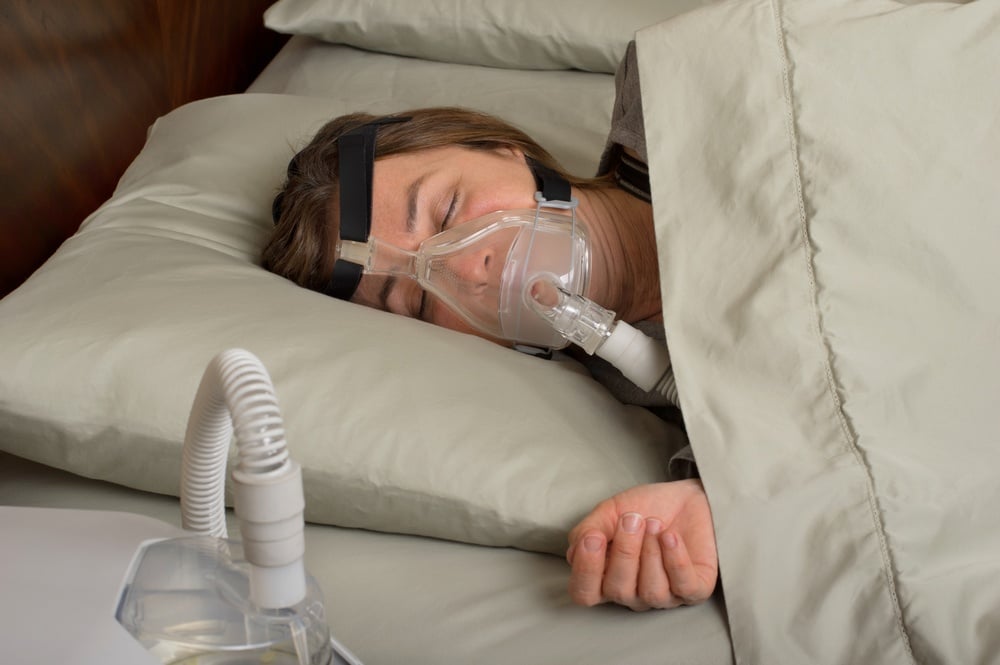
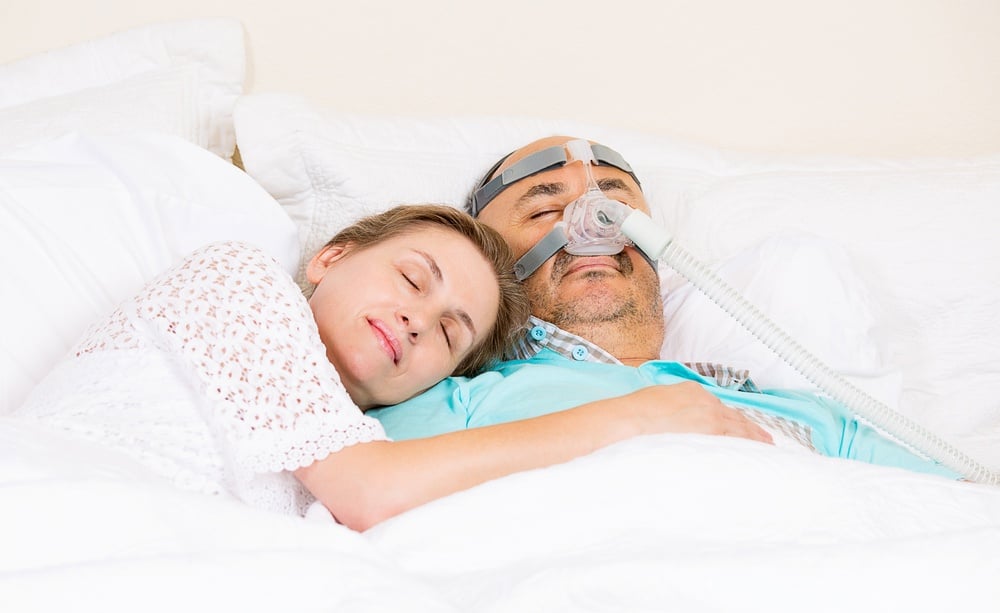
In the case of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), the therapy of choice is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which uses a mask to deliver pressurized air into the upper airway in order to add enough space and firm up the tissues to prevent dangerous pauses in breathing.
Wives are often the first to report that their spouses are heavy snorers, mostly because they have to listen to the noise most every night. If you're partner complains that you snore, and it's become a problem in your relationship, it's high time to do something about it.
At Sleep Resolutions, we can help you decide how to approach your snoring concerns with a quick call to one of our two convenient locations in Kansas (Garden City or Dodge City) at (620) 271-9400. Let us help you or your loved one take the next step to quiet, healthy sleep.













Leave a comment