Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can cause brain damage in human beings.
What is Brain Damage?
Brain damage is an injury to the brain that impairs its functions and is caused by destruction or deterioration of brain cells.
How Does Sleep Apnea Cause Brain Damage?
Sleep apnea is a breathing disorder that occurs during sleep. The airway going into the lungs become restricted or collapses completely for an extended period of time, stopping oxygen from getting into the lungs. This prohibits oxygen from getting into the lungs and being transported to the cells of the body, including the brain cells.
Oxygen is needed for proper functioning, and without it, brain cells will be damaged or die. Low levels of oxygen in the arterial blood is called hypoxemia. Hypoxemia can cause oxygen deficiency at the cellular level (called hypoxia). Hypoxemia and hypoxia are caused by respiratory disorders, the worst sleep-related breathing disorder being OSA.
During an apnea when oxygen is not able to get into the lungs, the heartbeat gets slower and slower. As soon as the person takes a breath, the needed oxygen gets into the blood and the heart begins pumping frantically to get the life-sustaining oxygen to all the cells. A few seconds later, the airway will collapse again, causing the heart to slow its pace again. Once another breath is taken, the heart will beat frantically again, transporting the oxygen to th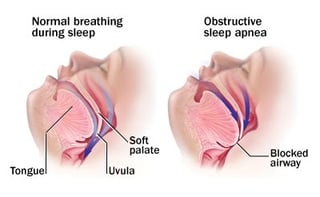 e cells.
e cells.
In very severe cases, this cycle repeats itself up to 80 or more times an hour. This feast-or-famine type of oxygen delivery system is difficult for the brain and other organs of the body to deal with, and the lack of oxygen causes cell damage to occur.
Sleep Apnea Side Effects
Sleep apnea causes oxygen starvation to the cells in the body and affects almost every organ in the human body. The brain is adversely affected by this oxygen deprivation just as much as any other organ. Here are some of the sleep apnea side effects on the brain and how they cause brain damage.
Blood-Brain Barrier
The blood-brain barrier is a capillary filtering mechanism that carries blood to the brain and spinal cord. It allows water, some gases, glucose and amino acids to pass through to the nerve cells, but it blocks the passage of certain dangerous substances, thus protecting the brain from infections, chemicals, harmful bacteria, and potential neurotoxins.
Sleep apnea causes the blood-brain barrier to become more permeable than normal. This increased permeability allows entry of damaging substances into the brain. Some of these invading substances may lead to epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, meningitis, Alzheimer’s disease and other serious conditions.
A study by Paul Macey, described in the Journal of Sleep Research, found that OSA sufferers have a weaker brain blood flow, indicating poor regulation of blood in the brain. The hypoxia from the OSA causes the combination of the irregular oxygen delivery system and the blood-brain barrier compromise to be a dangerous foe to the brain.
Hypoxia has been found to trigger inflammatory responses, irreversible atrophy and cell death. The neural changes that occur as a result of OSA likely contribute to central nervous system dysfunction, including both psychological and physiological conditions.
Brain Chemicals
Macey’s study found that two important brain chemicals were affected by the damage caused by OSA.
GABA (short for gamma-aminobutyric acid) acts as an inhibitor to slow things down and keep people calm.
Glutamate is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the nervous system. It is involved in cognitive functions such as learning and memory in the brain.
Mac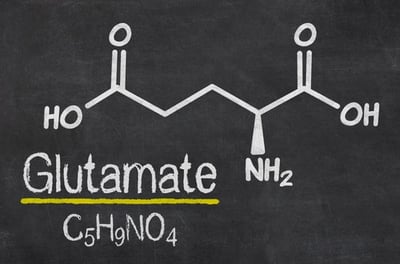 ey’s study found that sleep apnea caused substantial differences in the two chemicals that influence how the brain is working.
ey’s study found that sleep apnea caused substantial differences in the two chemicals that influence how the brain is working.
There was a drop in GABA, adversely affecting memory and learning, and causing a reorganization of how the brain works.
There was a great increase in glutamate. With the blood-brain barrier being compromised, the increased glutamate levels adversely affects the brain, causing toxic reactions and damage to nerves and neurons.
Gray and White Matter
The brain is made up of gray matter and white matter.
Gray matter refers to the cerebral cortex, where most information processing in the brain takes place. Gray matter is primarily associated with processing and cognition. It contains most of the brain’s neuronal cell bodies and involves muscle control, sensory perception such as seeing and hearing, speech, self-control, decision-making, memory and emotions.
White matter is the tissue through which messages pass between different areas of gray matter within the brain. It acts as a relay, a coordinating communication system between the brain regions. White matter actively affects how the brain learns and functions.
A study done by O’Donoghue found that sleep apnea impacts brain functioning and structure, causing injury to white matter axons and glia, and inflammation in the hippocampus.
Memory Loss
People with sleep apnea have difficulty converting short-term memory into long-term memory, causing forgetfulness. Memory storage occurs in the mammillary bodies of the brain. Dr. Seung Bong Hong’s research found that sleep apnea patients had nearly 20% smaller m ammillary bodies than normal sleepers.
ammillary bodies than normal sleepers.
Dr. Hong stated “Poor sleep quality could be responsible for poor memory, emotional problems, decreased cognitive functioning and increased cardiovascular disturbances.”
Damage to the white matter areas of the brain that regulate mood and memory have been shown in studies.
Dementia
sleep apnea causes sleep fragmentation, prohibiting the patient from getting into or staying in deep, restorative sleep. Rebecca Gelber did some unique research concerning changes in the brain leading to memory problems. Her team collected sleep test data on older men. The gentlemen later died, on average six years later.
Autopsies of the subjects found that those with the lowest blood oxygen levels at night (hypoxemia and hypoxia) were more likely to have brain damage from mini-strokes that often proceed dementia. The men who spent the least amount of time in deep, restorative sleep were more likely to show brain cell loss and brain atrophy.
Stroke
Sleep apnea affects the brain’s arteries, increasing the risk of stroke. In animal studies done at Randy Crossland at Baylor College of Medicine, it was found that “only one month of moderate OSA produces altered cerebrovascular function which could result in a stroke." In the animal study, mice’s “cerebral vessel dilatory function” decreased by as much as 22 percent.
In a Dresden University study led by Jessica Kepplinger, 91 percent of patients who had a stroke had sleep apnea and were likely to have white matter lesions and silent strokes. Greater than 33 percent of patient who had white matter lesions had severe sleep apnea and more than 50 percent of silent stroke patients had sleep apnea.
Silent strokes either have no symptoms or the person can’t remember having had the stroke. But silent strokes do cause permanent damage to the brain. The results of this study suggested that people with severe sleep apnea may have an increased risk of silent strokes and small lesions in the brain.
CPAP to the Rescue
The most significant effects of brain damage by OSA is impairments to cognition, mood and daytime alertness. Damage to gray and white matter in the brain can be reversed b y the use of CPAP.
y the use of CPAP.
Severe sleep apnea results in a significant reduction in white matter fibers in multiple brain areas.
In a study by Castronovo, after three months of patient-adherent CPAP treatment, limited improvements to damaged white matter brain structures were found, but after 12 months of CPAP treatment, there was a nearly complete reversal of white matter damage. Concurrently there were significant improvements in cognitive tests, alertness, mood and quality of life.
As to CPAP treatment on gray matter damage, improvements appeared after three months. Emotional functioning had the greatest improvement using CPAP therapy. Reduction in inflammation of the hippocampus structure, which controls mood regulation, showed normalization of that function. There was a great improvement in depressive symptoms.
It was indicated that repair and restoration of white matter in the brain takes up to a year with CPAP therapy but gray matter responds more quickly, taking only three months of CPAP therapy to regain normal functioning.
CPAP usage may bring the brain’s chemicals and functioning back to normal levels. With restoration of normalcy, the damaging, deadly symptoms of OSA reduce or resolve and the patient can regain physiological and psychological stability.
Sources:
Paul Macey, Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with low GABA and high glutamate in the insular cortex, Journal of Sleep Research, 2016.
Randy Crossland, Obstructive sleep apnea’s damage evident after 1 month, Baylor College of Medicine, May 9, 2012.
Jessica Kepplinger, High rate of sleep apnea in patients with silent strokes, Dresden University Stroke Center, Dresden, Germany, presented at International Stroke Conference, New Orleans, Louisiana, Feb. 1, 2012.
Vincenza Castronovo, White matter integrity in obstructive sleep apnea before and after Treatment, SLEEP, Vol. 37, No. 9, 2014.
Fergal J. O’Donoghue, Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in OSA before and after CPAP, SLEEP, Vol. 35, No. 1, 2012.
www.Wikipedia.com
Photo Credit: www.ShutterStock.com









Leave a comment